No one will ever deny the importance of having a data backup for business. It does keep you out of the danger zone in case you lose any important documents or information. But the question is can you rely on the backup drives forever, especially when there are cybercriminals everywhere?
Hacking has been taken to another level by the intruders, and now it has become more dangerous than ever. The existence of ransomware is the biggest threat to the business world, as it can encrypt all the files from the backups.
So if you are running your enterprise (no matter how big or small its operations are), you must think twice about your backup safety. And if you desire to secure your backup, then here’s all the important knowledge you must know.
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a type of malicious software used by cybercriminals to encrypt the victim’s data. Once the system is infected, the user loses access to all the files, which can only be restored when a ransom is paid to the attacker.
The victim is then given instructions for paying the ransom that is often referred to as a ‘fee’ to attain the decryption code. This ‘fee’ can cost around a few hundred bucks to thousands of dollars, which are paid through Bitcoin or similar platforms.
Ransomware spares no one whether it’s an individual or an organization. However, businesses are mostly affected as hackers are likely to receive a huge ransom amount.
There are different types of ransomware, such as WannaCry, Bad Rabit, and Jigsaw, and they have infected several businesses around the globe.
How Ransomware Encrypt Backups?
Backup is designed to secure businesses, but malware like WannaCry, Crypto, and Locky (different forms of ransomware) have been targeting the backup data. This is not a new phenomenon, in fact, the first-ever ransomware payment was made in 1989 that encouraged other hackers to follow the same footsteps.
Of course, it has been an easy but illegal and unethical way of earning billions of dollars. Cybersecurity Ventures predicted that 2019 would take away almost $11.5 billion from global businesses due to ransomware. And a report confirmed the loss of $7.5 to US organizations in the same year. Sadly, in all these cases, the majority of the attacks were made on firms’ backup.
But the question is how ransomware can encrypt your backups?
Well! There are three most common ways used by hackers to ransomware your backup.
- Networks
- Cloud Storage
- System Restore points
1. Traveling through Your Networks
Most ransom attacks are disguised as links, images, extensions, software setups, spam emails, attachments, and other documents, which are welcomed by the user itself through downloading, opening, or running the infected files. Nevertheless, hackers have found another way to contaminate your business, and it is through your network.
In this type of backup encryption, the intruders use your single computer system’s connection to find the rest of the computers, which are present on the same network. Once they get access, they damage all the systems including those with backups.
And the mission becomes quite easier when:
- The devices are connected to the internet without any strong protection program
- Outdated machines
- Files shared over shared networks
One of the best examples is of Ryuk ransomware incident that crippled several US businesses in August 2018. The estimated funds collected by the attackers were more than $600,000.
2. Syncing to Cloud Storage
Today, cloud storage is becoming a quick way to encrypt the files. According to McAfee, every one out of four cloud users has been a victim of data theft, as their copies over the cloud have turned malicious.
This signifies that your cloud storage is unsafe for ransomware attacks, as it keeps syncing with your local data storage.
For instance, a file share and sync solution like OneDrive and DropBox permit you to work on the files locally. And any amendments you make on your local files are synced right away to the cloud.
So when ransomware takes over, it rips through all your files locally and encrypts all of them. The same encrypted files are then synced to your cloud storage. This means that all your backups are polluted, causing a major loss to your business.
3. Deleting the System Restore Points
System Restore is an official feature of Microsoft Windows, which automatically backs up registry and system files on installing new drivers, and software, so that on finding any unusual change in your device’s performance, you can restore everything to the point when the new programs weren’t installed.
In other words, it helps individuals and businesses to create a restore point as per the date and time in case anything goes wrong due to any newly added files on the system, the old files could be recovered.
Unfortunately, this feature is also easily affected by ransomware, as the virus deletes all the restore points. WannaCry and GoldenEye are some of the prime examples of ransomware attacks, which took place in 2017, influencing 150 countries and encrypting 230,000 backups worldwide.
Backup Types and Methodology
Backup is a term that is now synonymous with data protection. Despite several backup types, there are four most prominent kinds of backup that every organization should be aware of. What are they and how they work? Here’s the answer.
- Full backups
- Incremental backups
- Differential backups
- Mirror backups
Full Backups
The most fundamental and complete backup type is the ‘full backup’. This type of backup is quite common in every business which includes copying of essential files to other media devices, such as a tape or disk.
The main benefit of full backups is that an entire copy of all the data is accessible on multiple sets of devices. However, the backup command must be given during each operation to secure the files on other devices. Also, it is a bit time-consuming and demands excessive storage space.
Incremental Backups and Differential Backups
In incremental backups, only the data that is modified since the previous backup is copied. The data could be of any type. Some businesses use this method to compare the timestamp of files from the current backup to the previous backup timestamps. Nevertheless, it is not that popular, but it saves storage as it only copies a fewer quantity (the latest changes) of data rather than the entire files from the beginning.
Differential backups are almost similar to incremental backups, as they copy all the changed data from the last backup. But each time it is operational, it continues to copy the entire data right from the beginning.
For example, you made the first backup (backup 1) on Sunday and made a second backup (backup 2) on Thursday, and on Saturday you created a third backup (backup 3). So the latest backup (backup 3) will include the data from both backup 2 and backup 1. This is why
On the contrary, an incremental backup will only include the data of backup 2 if the latest backup is ‘backup 3’. In the same way, if you will make backup 4 using the incremental backup method, then you will only find the data from a previous backup (backup 3). And you will need to peek into backup 3 to find the data of backup 2.
Mirror Backups
In mirror backups, you can backup any selected file faster than any other type. Nevertheless, once the source file is deleted, the saved file will be removed automatically.
Best Way to Ransom-Proof Your Backups
Despite the above-mentioned backup types can surely help you in various ways when it is about creating a backup, but the 3-2-1 backup rule is always superior and highly recommended.
3-2-1 Backup Strategy
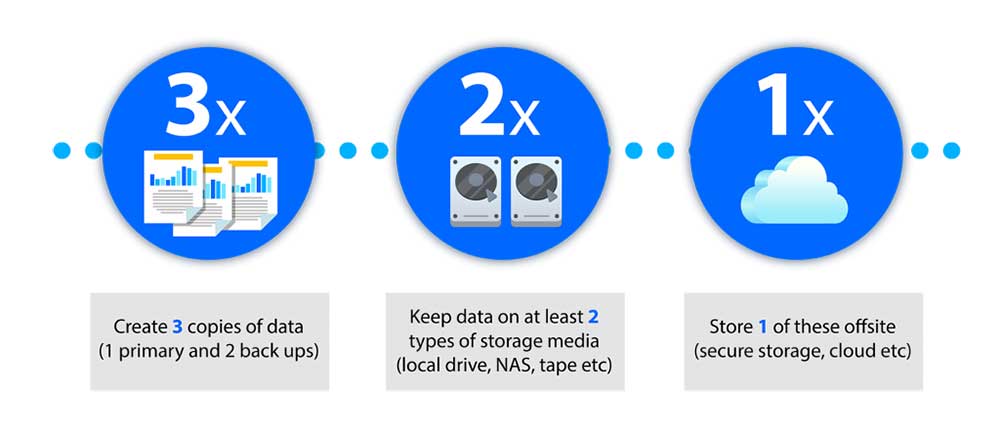
The 3-2-1 backup method is the easiest way to create a backup of all the important business data.
The rule is quite simple and it includes the following steps:
3: Make sure to create 3 copies of the essential data
2: Out of 3, make sure that 2 copies are stored on distinct storage media
1: The last one (1) should be kept away from the site (away from your office premises, etc)
The 3-2-1 is a blessing in times of emergencies like theft, natural calamity, and many more threatening incidents. So make sure you follow the rule to protect your organization’s important files.
Access Management
‘Access Management’, also called the ‘IAM’ or ‘Identity and Access Management’, is one of the greatest ways to prevent any business from ransomware attacks, as it identifies users and permits or blocks their access to any sensitive information. Therefore, it detects any strange activity or intrusion right from the beginning through the ‘Intrusion Prevention System’ or ‘IPS’. Moreover, its protection is stronger than firewalls.
The most effective IPS rules are predicated on Cisco Snort, and fortunately, Net Onboard offers the same rules to ensure instant response in case of threats, and to enhance network security.
Ransomware is a global threat to every business. Hence, it is in the best interest of your company to make sure the data is under strong protection. So if you seek safety and prevention from losing your information, you can always count on Net Onboard for top-notch services to secure your business from ransomware and other malware strikes.























