What is an SSL Certificate?
Most of you should know what is SSL certificate, millions of websites need an SSL certificate for their website security solution. Then, SSL is also used to secure credit card transactions, data transfer and login, and becoming a norm when securing browsing of social media sites.
In addition, SSL certificates always bind together with a domain name and an organizational identity. For businesses, they need to install the SSL Certificate onto its web server to initiate a secure session with browsers. All web traffic between server and browser will be secure once a secure connection is established. As you can notice the application protocol (HTTP) will change to HTTPS when a certificate is successfully installed, where the “S” stands for “secure”. Then, a browser will show a padlock or green bar in the browser when you visit a website that has an SSL certificate installed, it usually depending on the type of the certificate you purchase and the browser you use.
Besides, SSL -certificates are divided into three types: DV, OV, and EV SSL. You may be wondering which is the best SSL certificate that suitable for your website. You need to know more about the difference between the SSL certificate before you decide when to use it.
The difference between DV, OV, and EV SSL
Domain Validation (DV) SSL Certificates
Domain Validation has known as DV certificate, which is entry-level encryption used to secure a single domain. DV certificate is a fast and economical way to secure internet testing domains, personal websites, blogs, and other non-eCommerce sites. A DV SSL can secure both www and non-www domain versions.
Hence, you can secure your website in a few minutes by using DV certificates because validation is fully automated. DV certificates are issued very quickly as no company information is checked or displayed on the certificate.
![]()
![]()
Source: Google
The Validation Process of DV Certificates
Furthermore, the validation process of DV certificate is quite simple. The user must prove the domain ownership to the certificate authority (CA). SSL certificate authority can ask for email verification, file bases verification or domain registrar’s information to validate the domain. The certificate authority will send you an email to your email address with a confirmation link. You can click on the link by which the CA verifies your domain ownership. You should provide a valid email address and these are the examples:
In the file-based verification process, the CA will provide an HTML file along with Hash data. You should upload that file on your server’s root directory and wait for the process. The certificate will be issued once CA finds that correct file on your server. Moreover, you have to make sure that you kept domain registrar’s information public because CA will reject the issuance request if they find domain registrar’s information to be private.
Organization Validation (OV) SSL Certificates
Organization Validation also stands for OV certificates that contain legitimate business information, it is the standard type of certificate required for public-facing or commercial website which dealing with less sensitive transaction data. Besides, OV certificates conform to the X.509 RFC standards and thus contain all the necessary information to validate the organization. The cert is required for companies and organizations where users need to enter sensitive personal information such as contact information, credit card numbers and more.
Additionally, the OV certificate is more secure compared to DV certificate. The certificate authority, not only checking on the ownership of the domain name, but they will also carry out the additional vetting of the organization and individual applying for the certificate.
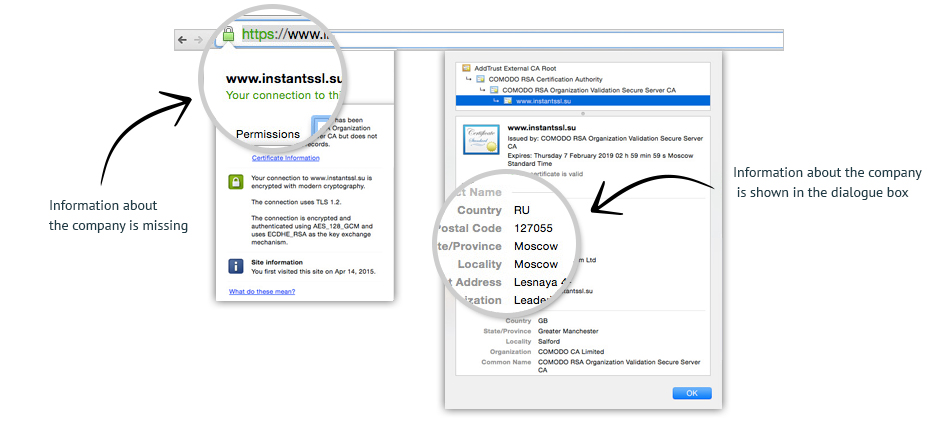

Source: leaderssl
The Validation Process of OV Certificates
Organization validation usually takes 1-3 working days for the verification process. It won’t be complicated if all the registration information is up to date. The purpose of having the verification process is to prove that you’re working for legitimate businesses. In fact, the organization validation process divides into 5 phases: domain ownership authentication, company verification, locality presence, telephone verification, and a final verification callback.
Domain ownership/authentication (DCV): This is to confirm ownership of a registered domain name. A Certificate applicant needs to verify the domain ownership by using DCV methods. The CA can verify your ownership by using email, file or CNAME-based authentication.
Company verification: This is extremely simple. The CA is just going to check your company’s registration information to make sure you’re a legitimate legal entity.
Locality presence: The CA will check the official registration documents and confirm the legal presence in your registered location.
Telephone verification: You need an organization’s active telephone listing in one of the acceptable online telephone directories.
Final verification callback: A final step in organization validation to reconfirm upon completion of all the requirements. The CA will send a final verification callback email once all the documentary validation is complete.
Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates
Extended Validation or EV certificates have the highest standard in SSL certificates as it provides the maximum trust to visitors. The vetting process of the EV certificate is more in-depth than other certificates, so it also requires the most effort by the CA to validate. Due to the trust and secure solutions, many world’s leading online businesses use EV as well. There is extra documentation that must be provided to issue an EV certificate by the CA.
Moreover, a site with an EV SSL certificate is the simplest to differentiate among the others. EV certificate displays a green browser address bar and a field appears with the name of the company, visitors able to know that you’re a legitimate organization.
Besides, EV certificate is not much more complicated than getting an OV certificate as the EV certificate has its value that’s more secure and trusted. Users will have more confidence as your website is secure.
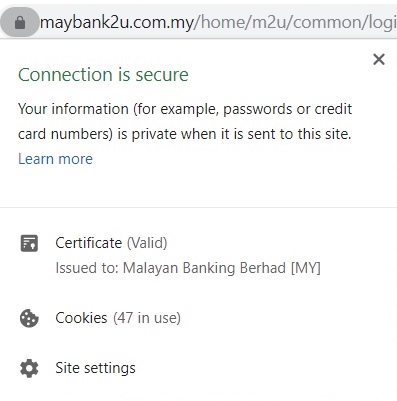

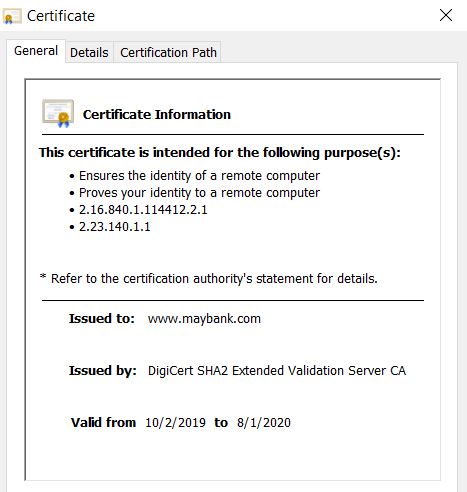

The Validation Process of EV Certificates
In addition, the verification process of EV certificate is more complicated because of the high- security standard on the internet. The extended validation process divides into 7 phases; EV enrollment form, organization authentication, operational existence, physical address, telephone verification, domain authentication, and final verification call.
The EV Enrollment Form: You need to fill out the form to show the CA that you are an employee and you’re authorized in making a purchase.
Organization authentication: The CA will check on your company registration information to verify that your company is legally registered.
Operational existence: The CA checks that your company has been operating for three years and above. If your business is not three years old, you need to furnish registration documents or a professional opinion letter.
Physical address: The CA will verify that your business has an established physical presence in the registered state or country.
Telephone verification: The Certificate authority verifies your organization has a working phone number listing in one of the acceptable online telephone directories.
Domain authentication: This is to verify that you’re the owner of the registered domain. Domain authentication is verified by the CA via email, cName or file-based authentication.
Final verification call: The CA will call the organization contact to verify the details of the order.
Which SSL certificate you should choose?
After you understand the difference between the types of SSL certificates, you can decide based on the situation of your website. For instance, you can use DV SSL to protect your personal blog because it is easy to obtain. If you’re hosting a company website, OV certificate is more recommended as it might be more suitable to protect the site. Additionally, if your site involved in handling credit cards and other sensitive data, you will need EV certificates that feature supreme protection for websites to keep all those sensitive private data secured.
Compare types of SSL Certificates
| Domain Validation | Organization Validation |
Extended Validation | |
| Suitable for | Small size website | Medium size website | Large Business Website |
| Types of Sites |
|
|
|
| Verification Process |
|
|
|
| Price | Cheap | Average | Expensive |
| Time required to issue certificates | Few hours | Several days | About a week |
| Address bar padlock | Available | Available | Available |
| Security trust seal | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Prove domain ownership | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Show Organization Identity-Info | No | Yes | Yes |
| Green Address Bar | No | No | Yes |
| Visitor Trust & Credibility | 2/10 | 6/10 | 10/10 |
Check out https://www.netonboard.com/security/ssl-certificates/ to get one of the SSL certificates that suits you the most to protect your site.























